Author: Yana Nencheva, Biochemist, PhD candidate in Biophysics
In recent years, the anti-vaccination movement has been gaining popularity and growing in numbers. False vaccination certificates issued by medical doctors to serve for children's enrollment in kindergarden or school, are not rarery spoken of. Children who are just waiting to reach adulthood to stand up to their parents and get vaccinated. These people began to associate with extreme vegetarians who protested for animal rights in the form of packaged frozen meat. They say they are conservationists. A distinction between between an ecologist and an environmentalist, or a homeopath, herbalist and nutritionist, becomes more and more vague and inintelligable for the general public
In this article, we will observe neutrality by explaining what alternative medicine is and point out all its 22 subtypes, referring to the classification of the National Medical Library of the United States - MESH (Medical Subject Headings) [ref. 1]. We will consider its benefits, for whom this type of treatment is appropriate and who should avoid it.
What is alternative medicine

By definition, alternative medicine is a set of therapeutic practices that are not currently part of the generally accepted allopathic medical practice. Two types are considered:
- When the alternative type of therapy is used in conjunction with classical (conventional medicine), it is called complementary (complementary) medicine.
- When the alternative type of practice is used instead of generally accepted medicine, it is called Alternative Medicine.
Some units of alternative medicine often lack sufficient scientific evidence, but since they have been applied for centuries, they are well studied in practice (e.g. curative diet, acupuncture). Other parts of it are not so prevalent (Dry Needling e.g.) and there is a tendency for these types of therapies to disappear and leave only a historical footprint.
What types of alternative medicine exist
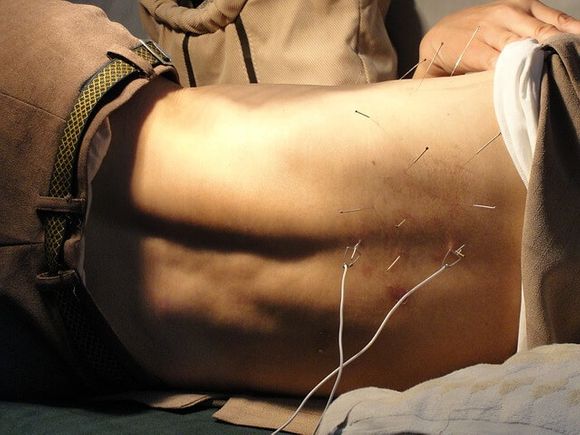
Some sources count down to 400-420 types of alternative practices, but officially according to the Classification of the National Medical Library, there are 22 basic subtypes of alternative medicine.
1. Acupuncture - from Latin acus, "needle" and punctura "pricking", is a technique for treating disease by placing needles on certain, according to the disease, acupuncture points on the body. Sometimes used in combination withheat, herbs, acupressure and electrical stimulation.
2. Anthroposophy – from Greek "anthropos" – man and "sofia" – wisdom is a spiritual, mystical doctrine founded in 1912.
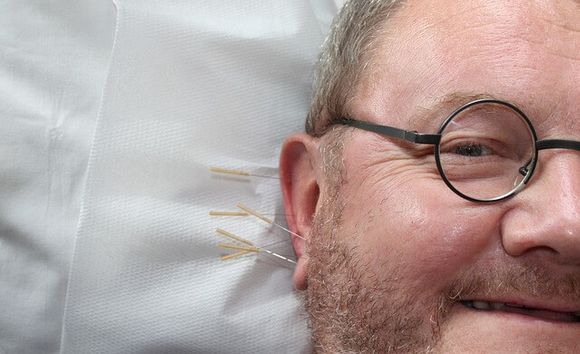
3. Auriculotherapy - a form of acupuncture, but the impact is only on points of the ear to treat other parts of the body.
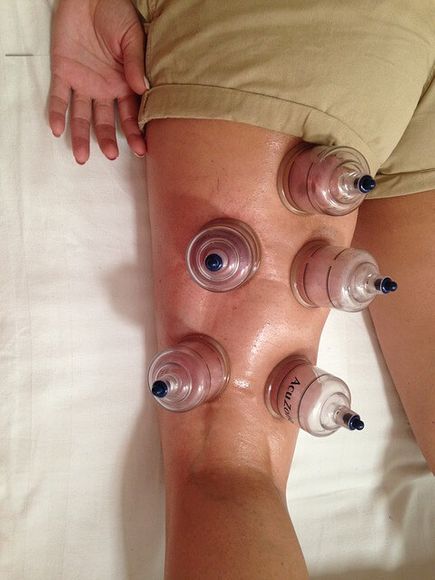
4. Cupping therapy - the practice involves placing cups on the skin to create a vacuum, which is believed to help increase blood flow and promote healing.
5. Pain inhibiting pain (Diffuse Noxious Inhibitory Control, DNIC or conditioned pain modulation (CPM) - a physiological process in which pain in one part of the body is inhibited (suppressed) by deliberately submitted another painful stimulus induced elsewhere in the body.
6. Dry Sewing (Dry Needling) - the intervention is performed with a thin needle that passes through the skin and affects specific muscle points in order to treat neuromuscular-skeletal pain and movement damage. The procedure is performed by qualified physiotherapists with additional training certification. The pain of the intervention is expected to be minimal and relax in a few seconds.

7. Holistic medicine - according to her, people function as complete, integrated units, and when something is wrong, then the problem is in the whole; in her opinion, the disease is just one manifestation of a complete problem in life force.
8. Homeopathy - the founder was Samuel Hahnemann in 1796, and the concept is to treat diseases with the highly diluted form of the substance causing the disease in question.
9. Horticultural therapy - a therapeutic approach in which gardening is used to reduce stress, improve social, emotional, psychological and physical health.
10. Integrative oncology - is based on therapies to reduce symptoms associated with the treatment of cancer.
11. Traditional medicine - based on beliefs and practices passed down from generation to generation , includes mystical and magical rituals, phytotherapy and other treatments that modern medicine cannot explain.
12. Mesotherapy - vitamins, extracts or other bioactive substances are used for local treatment with subcutaneous injections or perfusion of substances in the different layers of the skin under the epidermis.
13. Therapies of the mind and body - methods or techniques of treatment, which are based on knowledge of the relationship between mind and body. These techniques often include ways to lower tension and stress in order to improve emotional, mental and physical healing.

14. Musculoskeletal manipulations - various manipulations of body tissues, muscles and bones, with only hands or with the use of special equipment.
15. Naturopathy - based on the belief that diseases can be cured or prevented without taking any medications. Treatment through a healthy lifestyle (clean water, air, sun), specific diet, exercise and massages.
16. Organotherapy - a technique that uses animal organs, extracts and especially glands.

17. Phytotherapy - this is a treatment with the use of plants or herbs. Aromatherapy is also part of this group, except for the group of Therapies of mind and body.
18. Prolotherapy - This is one of the promising therapies with an 85-95% success rate.
19. Reflexology (Reflexotherapy) - this is a local therapy, in which pressure is applied at certain points.
20. Sensory art therapies - therapies that use different types of art, as well as those using the senses.

21. Speleotherapy - in this type of therapy, conditions characteristic of caves (illumination, humidity) are reproduced and salt pans are made. This practice is used in a narrower range of medical conditions, mostly respiratory and skin conditions. It is believed that standing the patient in the salt shaker reduces irritations and the symptoms of the disease decrease or disappear.
22. Spiritual therapy - includes a mix of mystical, religious, spiritual practices for healing purposes.
What are the benefits of alternative medicine

"What are the benefits of alternative medicine?" is a difficult question that cannot be answered unambiguously, with a variety of methods. From a historical pointof view , until a very late stage of the scientificdevelopment of mankind, it was not possible to develop classical medicine as we know it today.
Prehistoric medicine used herbs, potions, spiritual practices and rituals led by priests and shamans, which is quite natural.The translation of the papyrus can be found HERE and you can look at a case for the diagnosis and treatment of the sick. until [ref. 2] is strengthened.
Over the years, science has begun to "check" alternative treatment practices to explain exactly how they work.
For whom is alternative medicine treatment appropriate

In many cases, people are resorting to alternative treatments where classical medicine can no longer help and use unconfirmed or hesitant science-denied practices.It gives hope. Whether treatment is appropriate - sometimes it becomes a matter of personal choice.
In fact, alternative medicine refers to a centuries-old "sample error" and if the medical practice is proven not to be harmful, It is quietly used, even if its positive result is not sure.
For whom is alternative medicine treatment contraindicated

Given that there are 22 types of categories and about 400 types of practices, it is not possible to say who alternative treatment is contraindicated for. This is an issue that depends on the type of therapy and on very many individual factors . Patients trust the doctor whotrusts them.
In India, people do not trust classical medicine and would prefer a healer in the spiritual sense of the word than to be treated by a doctor in a clinic. In China, healers pass on the knowledge of Traditional Chinese Medicine generation to generation, from teacher to apprentice, for centuries and there, too, classical medicine is not so imposed. With us in Bulgaria it is only natural not to trust people who practice acupuncture or Indian healing practices after only 2-3 years of training.
Finally, when we wonder whether to turn to alternative medicine, let us know thatclassical aims to be the most humane type of treatment at the heart of which is the Hippocratic Oath with "Primum non nocere", translated "First, do not harm" [ref. 3].
Read more:
Parsley, celery and other herbs that help fight cancer
What are the causes of enlarged prostate and is there treatment with herbs