What are COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2
COVID-19 is a pandemic disease and is caused by infection with the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. Coronavirus also causes a higher rate of serious illness and death compared to the flu. But symptoms can vary greatly from person to person. This virus spreads mainly by respiratory means - through droplets of saliva or excreted from the nose when an infected person coughs. [ [ref. 1] ]
SARS-CoV-2 is a member of a large family of viruses called "coronaviruses". These viruses can infect humans and some animals. Sars-CoV-2 was first known to infect humans in 2019. However, cases of morbidity have not yet been completely zeroed in, and some therapeutic approaches include both medications and herbal products. One of them, which has been studied for its potential against COVID-19, is ginger.
What are the health benefits provided by ginger
The health benefits of ginger are painkillers, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating. In particular, the beneficial properties of ginger are shown in patients suffering from osteoarthritis, neurodegenerative diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, type 2 diabetes, respiratory distress, liver diseases and primary dysmenorrhea. Ginger, or more precisely its compounds, exhibit a strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant influence in numerous animal models. [ [ref. 3] ] Experimentally and clinically ginger (the rhinity of Zingiber officinale) exhibits numerous therapeutic actions, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulating, antimicrobial, antifungal, anticancer, neuroprotective, antimygrenosis, hepatoprotective, respiratory, antidiabetic effects. [ [ref. 4] ] In this regard, ginger also shows direct antiviral effects and may have a protective role against ARDS, which is the main cause of mortality in patients with severe COVID-19. ARDS - Acute respiratory distress syndrome, is an acute respiratory distress syndrome and a serious lung condition that causes low levels of oxygen in the blood. [ [ref. 5] ] Due to its antiviral action, ginger can have a beneficial effect on many organs that are affected by SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Chemically speaking, ginger contains over 400 different compounds, but its pharmacological effects are largely due to its terpenes and phenolic compounds. The terpene ingredients of ginger include zingiberen, bisabolic, farnesen, cesifelandren, limoneol, linalool, borneol, geranial and curcumen. Phenolic compounds derived from ginger include gingerols, paradoli, shogaoli and zingeron. [ [ref. 6] ]
Evidence of the potential of ginger against COVID-19 and other viruses
Fresh ginger has powerful antiviral effects against human respiratory singial virus (HRSV) and rhinovirus, as well as against several subtypes of influenza virus A. Results of in vitro experiments show that gingerol directly inactivates hepatitis A viruses and inhibits the replication of human norovirus in an infected cell line. In addition to direct antiviral effects, ginger can multiply congenital antiviral immunity. IFN is the first protective line against viral infections and in vitro analyses show that gingerols promote the secretion of IFN-γ by activated T cells. In addition, fresh ginger extract stimulates the secretion of IFN-α and IFN-β of HRSV -infected epithelial cells.
With regard to coronavirus, the SARS-CoV-2-related papain-like protease (PLpro) cleaves polyprotein a/b (PP a/b) in different locations, giving several proteins needed for survival and replication of the virus. By molecular modeling, it becomes clear that 8-gingerol, 10-gingerol, 6-gingerol and another class of ginger ingredients strongly inhibit PLpro. They also found that 6-gingerol exhibits a high affinity for binding to a number of viral proteins (main protease, molecule such as SARS-CoV3C and catepsin K), which are essential for SARS-CoV-2 replication.
Meanwhile, some of the other terpenes such as geraniol, shogaol, zingiberen, zingiberenol and zingerone may interfere with the binding of S protein-ACE2. The results of a computational analysis show that the turpene derived from ginger, namely sesquifelandren, binds to the S protein and thus interferes with the interaction S protein-ACE2.
However, it is important to note that these study data should be supported by in vitro and in vivo observations .
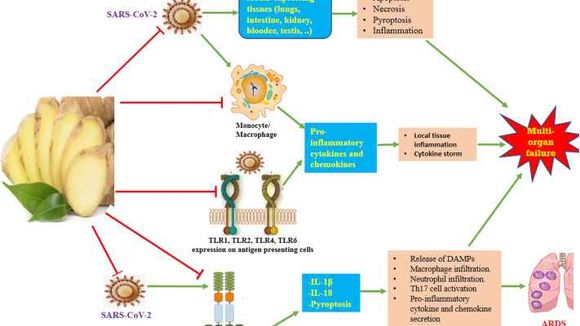
Inflammation-mediated effects of SARS-CoV-2 on COVID-19 pathogenesis