What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition that leads to too high blood sugar levels. Sugar in the blood is also known as glucose, it is the main source of energy for your body. Sugar comes from the food you eat, especially from carbohydrates found in foods such as bread, rice and potatoes.
Glucose is carried through the blood to cells in the body to give them energy to work. When glucose is present in the blood, the pancreas produces a hormone called insulin. Insulin tells the body's cells to absorb glucose and use it as energy. 1
In a person with diabetes, his body can not absorb glucose because he has a problem with insulin. This means that:
- cells do not use glucose for energy;
- unused glucose remains in the blood and accumulates;
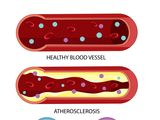
- excess glucose can damage the arteries (arteries carry oxygen-rich blood and nutrients throughout the body);
- If the arteries are damaged, it can increase the risk of developing heart and circulatory diseases.
How is diabetes treated?
Treatment for type 1 and type 2 diabetes may be different. Surely, a healthy balanced diet and physical activity are recommended to help treat both types, especially type 2. This is because type 2 diabetes is associated with being overweight or obese.
People with type 1 diabetes cannot produce insulin because their body attacks the cells that produce it. This means that their body needs to get insulin to control their blood sugar levels. And they need to monitor their blood sugar levels several times a day. Treatment in people with type 1 diabetes is through insulin injections several times a day, regular exercise, and a healthy balanced diet.
In turn, most people need medication to control their type 2 diabetes. The drug helps to lower the amount of sugar in the blood. This can reduce the risk of developing other health problems, such as heart and circulatory diseases. Treatment for type 2 diabetes is usually medicated and is based on regular exercise and a healthy balanced diet.
Herbal and natural therapeutic agents for diabetes

Some common herbs and spices have blood-sugar-lowering properties, making them beneficial for people with or at high risk of type 2 diabetes.
In recent years, a number of clinical studies have been conducted that have shown potential links between herbal therapeutics and improved blood glucose control. This has logically led to an increase in people with diabetes using these natural solutions to alleviate the condition and accompanying symptoms.
Plant-based therapies that some studies have shown to have antidiabetic properties include:
- Aloe vera
- Blueberry extract (Vaccinium)
- Bitter melon (Cucumis melo)
- Cinnamon verum
- Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum)
- Ginger (Zingiber officinale)
- Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus)
Although such therapies are commonly used in Ayurvedic and Eastern medicine to treat serious conditions such as diabetes, some health experts still remain skeptical about their medical benefits.
Some herbs, vitamins, and supplements may interact with diabetes medications (including insulin) and increase their hypoglycemic effects. Therefore, their intake should always be discussed with a doctor first to make sure that they are safe for your condition and to determine the appropriate dosage.
The herbs and herbal remedies listed below have been used traditionally by local people to treat diabetes in the areas where they grow.
Garlic (Allium sativum)

Garlic (Allium sativum) has antioxidant properties and immunomodulatory effects. Although few studies have directly linked garlic to insulin levels and blood sugar levels, the results are positive. [ref. 1]
Garlic can cause a decrease in blood glucose, increase secretion, and slow down the breakdown of insulin. However, limited data are available and further studies of these effects are needed.
Bauhinia forficata and Myrcia uniflora
The Brazilian orchid tree (Bauhinia forficata) grows in South America and is used in Brazilian traditional medicine. This plant is called "vegetable insulin". Myrcia uniflora is also widely used in South America. Studies using herbs as tea infusions have shown that their hypoglycemic effects are slightly weaker than expected, but still have them.
Indian coccinia (Coccinia indica)
Indian coccinia (Coccinia indica) grows freely in the Indian subcontinent. Traditionally used in Ayurverdic medicines, the herb has been found to contain insulin-mimetic properties (i.e., mimicking the function of insulin).
Significant changes in glycaemic control have been reported in studies involving coccinia indican, and experts believe it should be investigated further. 3
Ginseng
Ginseng (Panax) is a collective name for various plant species - there are Siberian ginseng (Eleutherococcus senticosus), Indian ginseng (Withania somnifera), American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius) and others.
In some studies using American ginseng, a decrease in fasting blood sugar has been reported. Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng), Siberian ginseng, American ginseng, and Japanese ginseng (Panax japonicum) were used in these studies.
In some areas, the plant, especially the Panax species, is hailed as a "medicine for everything." As is the case with many of the herbs used around the world in the treatment of diabetics, further long-term studies are needed to test the efficacy of each type of ginseng.
Gymnema sylvestre
Gymnema sylvestre is also used in traditional Ayurvedic medicine. The plant is found in the rainforests of southern and central India and has been linked to a significant decrease in blood sugar. Some animal studies have even reported islet cell regeneration and increased beta cell function. 4
The active compound of the plant is a group of acids called gymnemic acids. Gymnemic acids have antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory effects. The antidiabetic set of molecules was identified as a group of closely related gymnemic acids after being successfully isolated and purified from the leaves of G. sylvestre.
Bitter melon (Momordica charantia)
Momordica charantia is found under different names and grows in some areas of Asia, India, Africa and South America. It has been found that prepared in different ways can help diabetics with insulin secretion, glucose oxidation and other processes.
Bitter melon has also been reported to have antiviral, antibacterial, anticancer and immunomodulatory properties. It is widely used as an adjunct or alternative therapy for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in many countries, including Korea. 5 However, more studies are needed on the potential action in the areas listed.
Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum)
Trigonella foenum graecum is an herb known as fenugreek and is widely grown in India, North Africa and parts of the Mediterranean. It is also part of Ayurvedic medicine and is widely used in cooking.
Of the few uncontrolled studies that have been conducted on type 2 diabetics, most report improved glycaemic control. More in-depth studies are certainly needed.